
The maximum collector current Ic(max) for any Darlington pair is the same as that for the main switching transistor, TR 2 so can be used to operate relays, DC motors, solenoids and lamps, etc. The base of the Darlington transistor is sufficiently sensitive to respond to any small input current from a switch or directly from a TTL or 5V CMOS logic gate. This then makes darlington transistors ideal for interfacing with relays, lamps and motors to low power microcontroller, computer or logic controllers as shown. Then we can see that a darlington pair with a gain of 1,000:1, could switch an output current of 1 ampere in the collector-emitter circuit with an input base current of just 1mA. The advantage of using an arrangement such as this, is that the switching transistor is much more sensitive as only a tiny base current is required to switch a much larger load current as the typical gain of a Darlington configuration can be over 1,000 whereas normally a single transistor stage produces a gain of about 50 to 200. For example: the NPN TIP120 and its PNP equivalent the TIP125. Darlington transistor pairs with current gains of more than a thousand with maximum collector currents of several amperes are easily available. Then we can see that for two identical transistors, β 2 is used instead of β acting like one big transistor with a huge amount of gain. Then transistor TR1 is connected as an emitter follower and TR2 as a common emitter amplifier as shown below. In some cases where the current gain of a single transistor is too low to directly drive a load, one way to increase the gain is to use a Darlington pair.Ī Darlington Transistor configuration, also known as a “Darlington pair” or “super-alpha circuit”, consist of two NPN or PNP transistors connected together so that the emitter current of the first transistor TR 1 becomes the base current of the second transistor TR 2. A typical value of β for a standard bipolar transistor may be in the range of 50 to 200 and varies even between transistors of the same part number. The ratio of collector current to base current ( β ) is known as the current gain of the transistor.

Then we can see that a smaller current flowing into the base terminal can cause a much larger current to flow between the collector and the emitter. A higher voltage causes an increased base current, Ib to flows into the device resulting in collector current Ic becoming large while the voltage drop across the colletor and emitter terminals, Vce becomes smaller. However, the transistors base terminal needs to be switched between zero and some positive value much greater than 0.7 volts for the transistor to fully conduct. If we operate the transistor between these two modes of cut-off and conduction, the transistor can be made to operate as an electronic switch. The transistor is now said to be switched “ON” (conducting). If we now forward biased the base terminal with respect to the emitter by using a voltage source greater than 0.7 volts, transistor action occurs causing in a much larger current to flow through the transistor between its collector and emitter terminals. As the base terminal is grounded, no current flows from the collector to the emitter terminals therefore the non-conducting NPN transistor is switched “OFF” (cut-off).
#Npn darlington transistor switch configuration series
One difference to consider when using Darlington transistors over the conventional single bipolar types when using the transistor as a switch is that the Base-Emitter input voltage ( V BE ) needs to be higher at approx 1.4v for silicon devices, due to the series connection of the two PN junctions.When the base terminal of the NPN transistor is grounded (0 volts), zero current flows into the base therfore Ib = 0. As well as its high increased current and voltage switching capabilities, another advantage of a Darlington transistor switch is in its high switching speeds making them ideal for use in inverter circuits and DC motor or stepper motor control applications. The first or “input” transistor receives an input signal, amplifies it and uses it to drive the second or “output” transistors which amplifies it again resulting in a very high current gain.
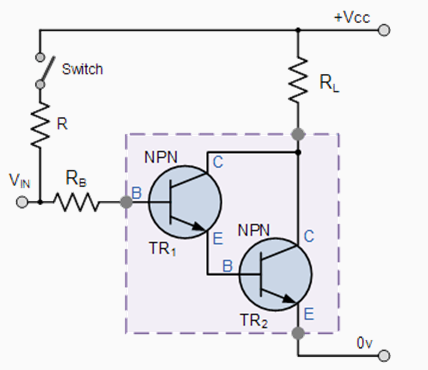
The above NPN Darlington transistor switch configuration shows the Collectors of the two transistors connected together with the Emitter of the first transistor connected to the Base of the second transistor therefore, the Emitter current of the first transistor becomes the Base current of the second transistor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
